About this event
The CIGRE UK D2 Digitalisation & Data Science – Enablers for Net Zero Conference took place on Friday, 6th December 2024, kindly hosts at Imperial College London. This one-day event brought together leading experts, innovators, and key stakeholders from the energy and digital technology sectors to explore how digitalisation and data science are unlocking new opportunities in the drive towards achieving net zero.
With the urgent need to decarbonise and modernise energy systems, the power sector is experiencing a rapid transformation. The integration of digital tools, advanced information systems, telecommunications, and robust data management practices is critical for the efficient operation, control, and management of electrical power systems. Cybersecurity has also become a central concern, ensuring that these digital infrastructures are resilient and protected against growing threats. The conference discussed the latest innovations and initiatives that are shaping the future of energy.
Pioneering projects and technologies that demonstrate how digital solutions can propel the energy transition forward, improving the reliability, efficiency, and sustainability of power systems were reviewed and discussed. Through a series of expert presentations, engaging panel discussions, and valuable networking opportunities, attendees gained crucial insights into how digitalisation and data science are enabling the energy sector to meet ambitious carbon reduction targets and beyond.
Click on the agenda titles below to view/download the presentations
Agenda
09:00 – Arrival Refreshments
09:30 – Introduction to Study Committee D2 | Jianing Li, CIGRE UK D2 Regular Member
09:45 – Working Group D2 57 – CIM (Common Information Model) | Siva Kaviya Trichy Siva Raman, National Energy Systems Operator
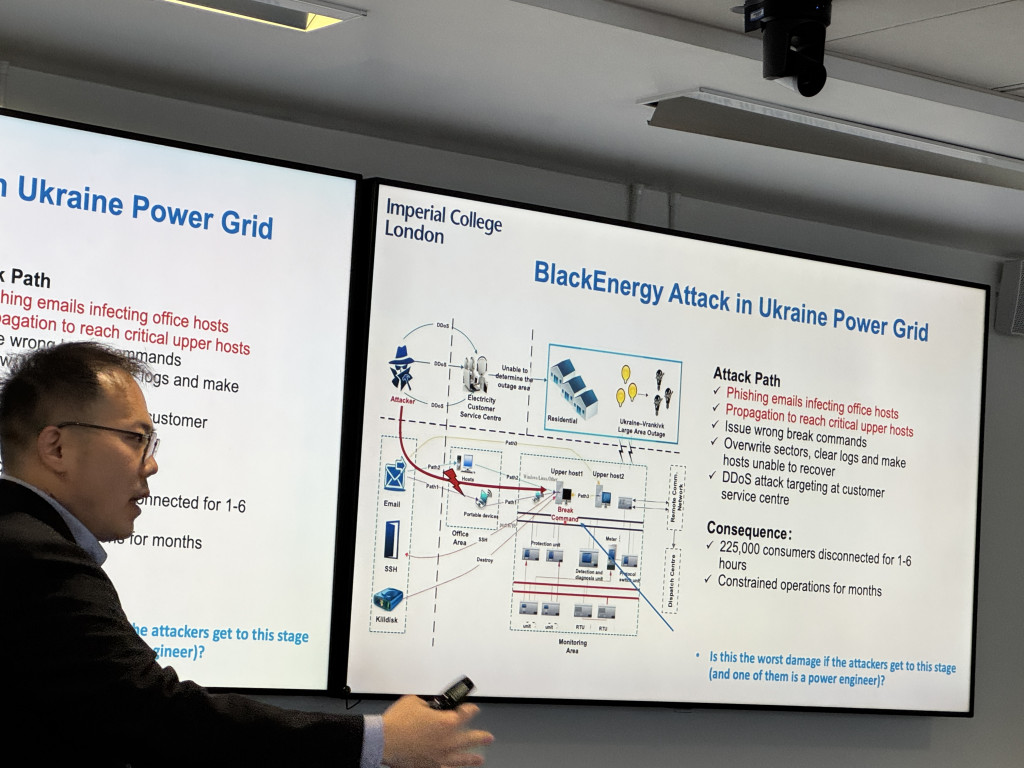
10:00 – Cyber-resiliency of digitalised power grids | Dr Fei Teng, Imperial College London
10:20 – Digital Substations – A Summary of UK Power Network’s Project Constellation | Oussama Yousfi, UK Power Networks
10:40 – Cyber Security for Active and Flexible Energy Networks (Cyber-SAFEN) | Haiyu Li, University of Manchester
11:00 – Comfort/Refreshment Break
11:20 – 1st Panel/Q&A
11:40 – Pole Defect Image Detection Model | Emerson Smith, National Grid
12:00 – Enhanced Information and Data Exchange to Enable Future TSO-DSO Coordination and Interoperability | Gareth Taylor, Brunel University London
12:20 – Buffet Networking Lunch (one hour)
13:20 – Using AI:ML to Enhance the OPEX and CAPEX of Grid Operations | Sihu Chen, GE Vernova
13:40 – Automated Corrosion Assessment and Forecasting at National Grid (presentation not available at this time) | Amjad Karim, Keen AI
14:00 – Digitalisation of transmission substations with an emphasis on protection and automation | Peter Crossley, University of Manchester
14:20 – 2nd Panel/Q&A
14:50 – Wrap up
15:00 – Depart
Introducing CIGRE UK Study Committee D2
CIGRE SC D2 which focuses on Information Systems, Telecommunications, and Cybersecurity for electric power systems. As a key area of expertise within CIGRE, SC D2 is dedicated to addressing critical topics at the intersection of technology and energy, including:
- Cybersecurity and Resilience: Protecting and strengthening critical infrastructure against emerging threats.
- Advanced Telecommunications: Enabling secure, reliable communication systems to support grid operations.
- Information Systems and Digital Transformation: Supporting IT/OT convergence and adopting new technologies for operational efficiency.
- Big Data, Analytics, and AI: Harnessing data-driven insights for enhanced system reliability and performance.
SC D2 provides a platform for professionals to collaborate, share knowledge, and develop solutions to address the challenges shaping the future of the energy sector.
We are actively organising events to facilitate learning and collaboration, including:
- Webinars and technical Presentations: Focused discussions on emerging trends like cybersecurity in power systems and telecommunication innovations.
- Workshops and conferences: Interactive platforms to exchange ideas and solve practical challenges.
- Networking opportunities: Connect with experts, stakeholders, and peers across the energy sector.
More information about our events and activities can be found on our website.
As a foundational enabler, SC D2 works closely with other Study Committees to address interdisciplinary challenges, such as:
- Asset Protection and Monitoring (SC B5): Supporting protection systems with secure and reliable communication networks.
- System Operation and Control (SC C2): Enhancing operational efficiency by integrating asset health data into system-wide decision-making.
- Technical Performance (SC C4): Improving asset reliability through advanced diagnostics and system performance analysis.
- Distributed Energy Resources Integration (SC C6): Facilitating secure integration of distributed assets with robust IT and telecom solutions.
Join Our Mailing List
To keep up with the latest developments, I invite you and your colleagues to subscribe to our CIGRE UK Mailing List and CIGRE UK SC D2 Mailing List. Subscribers receive:
- Regular updates on cutting-edge research, technical advancements, and working group outcomes.
- Invitations to upcoming webinars, workshops, and other professional events.
- Access to valuable resources, including reports and technical insights.
Please feel free to share this mailing list subscription link with anyone in your network who may find our work valuable.
I would also love to discuss how SC D2 can support your work or how we might collaborate to advance our shared goals in information systems, telecommunications, and cybersecurity for power systems. Please feel free to reach out with any questions or ideas.
Jianing Li: CIGRE UK D2 Regular Member